What Is This Feel-Good Video Really About? (Part 1 of 2)
Do you have seven minutes to watch a sweet film about a dolphin rescuing a dog who is swept off a boat in shark territory? (If you don’t, you can skip some great dolphin footage and start 2 minutes, 20 seconds in, as the dog goes over the stern, and cut off at 4:45, after the animals have made their sweet farewells. Surely, you have 2 minutes and 25 seconds you can spare. And feel free to turn off the sound. It’s just music, and repetitious music at that.) Makes you feel warm and fuzzy all over, right? Personally, I love videos about interspecies friendship, and I’ve seen a bunch of them over many years.
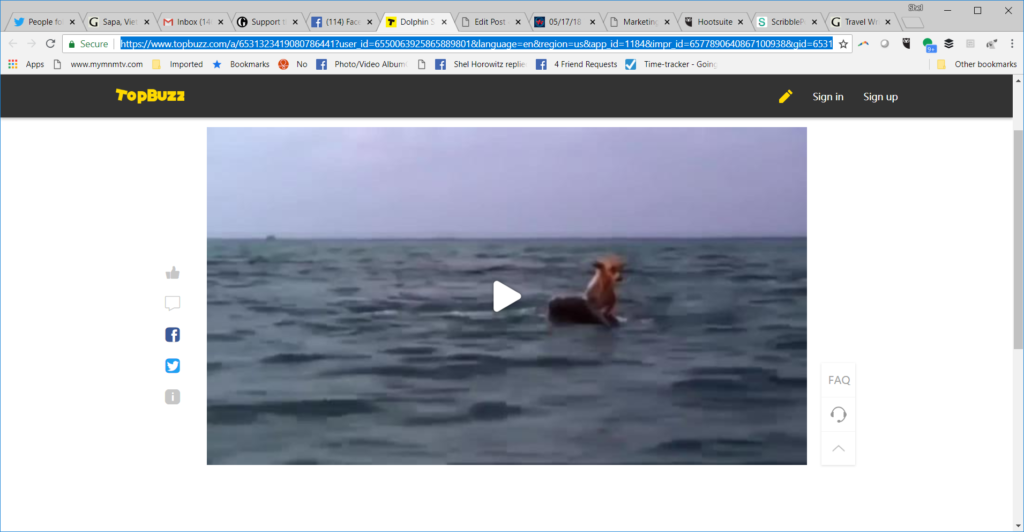
Now: do you think this is an actual event, a recreated actual event, or fiction? Why? Please share your thoughts in the comments before reading further. Then scroll down and continue to see my answer–and my reasons.
Now read my take on it:
I’m pretty sure it’s fiction. And I’m concerned that there’s no text with this film, and no credits at the end–in other words, no accountability. I have no objection to filming heartwarming works of fiction. I love that sort of thing, from Frank Capra’s “You Can’t Take it With You” to “Fried Green Tomatoes” to “Life Is Beautiful” and “Jude”. But all of these are clearly marketed as story, not fact.
In my opinion, this film is specifically designed to make most viewers believe this was a real event.
And I have trouble with that. I feel its “story-ness” should be disclosed, and we should also know who produced the film. I’ll tell you why in a moment, but first, here’s how I reached my conclusion.
Why You Can’t Necessarily Trust Your Eyes
Because I’m trained in journalism and have worked for decades in marketing, I ask hard questions about what is and isn’t real, what people’s motivations or agendas are, and how to filter information based on what’s really going on versus what the speaker or writer or photographer or filmmaker is trying to get you to think is going on.
If you watch any crime movies from the 1930s through 1950s, there’s a pretty good chance that the detective will turn to the suspect and shout, “photos don’t lie!” But here’s the thing: THAT is a lie. Photos can lie in what they choose to include or not. A famous example: the close-ups of a statue of Saddam Hussein being felled by a jubilant (and apparently huge) Baghdad crowd were discredited by wide-angle shots showing only a couple of hundred people, many of them US soldiers rather than locals. The close-ups were propaganda, not truth, even though the photos themselves were real and unretouched. And even in the 1950s–for that matter, even in the 1850s–there was a whole industry around photo alteration. This was true in film as well; ever hear the expression “left on the cutting room floor”? The technologies of photo editing and film editing go back to the earliest days of photography and filmmaking.
In today’s digital world, tools like Photoshop and video editors have transformed those doable but difficult tasks into something incredibly easy, and only an expert will be able to tell. So in this era, we can never trust that a picture or a movie is accurate unless we were there when it was shot. Thus, unfortunately, we need to bring a certain amount of critical analysis when we view any video, any photograph.
And through this lens (pun intended, I confess), when I watch this video, I immediately discard any idea that we’re watching real-time true-story footage.
Why?
7 Reasons Why I Think It’s a Fake
- It’s waaaay too slick. This is professionally shot and carefully edited, by a skilled camera operator using high-resolution equipment, tripods, and lighting to produce footage as good technically as anything coming out of Hollywood. In real life, this would have been shot on a cell phone, held in a hand that shook at least a little. It’s on a moving boat, after all.
- Much of the footage is underwater or behind the boat the dog was riding, yet no other boats are visible.
- When the dog slips off the deck into the water, no people are around. If anyone were filming an actual event, we’d see some kind of rescue attempt, and we certainly would not see the boat blithely continuing away, stranding the pet. At least the crew of the videography boat would get involved.
- It’s just too convenient that cameras happened to focus on all the key places. And yes, that’s a plural. There was one camera focused on the boat deck and later on the swimming dog, and at least one other one focused underwater at the dolphin and shark.
- If the shark were really close enough to attack the dog, it would have gone after the dolphin too. Giant sharks don’t care much about “collateral damage.”
- It strains credulity that the boat would be waiting, unmoving, in still water, just when the dolphin deposits the dog on the tailgate, considering there are plenty of waves in the dolphin-carries-dog footage.
- I’m suspicious of the site it’s on, something called TopBuzz, which I’ve never heard of. I didn’t notice at first when I clicked the link from a Facebook message that it had a monstrously complex tracking URL, too. Uh-oh! I’ve stripped those tracking codes out of the URL as here. To its credit, it doesn’t try to get me to watch all sorts of salacious videos, and a search for complaints brought up only questions about its relationships with content creators, not viewers. And I checked for viruses after having the page open for several hours while writing this, and it came up clean.
I’m also skeptical that this is a later recreation of a true event, although I’d grant that maybe a 10 percent chance. Why? Because much of the footage “documented” events with no witnesses. Unless one of the human crew is fluent in either dog or dolphin language, neither party could have told the story. And the dog might not even know about the shark threat. Certainly the humans in the boat that drove away would have no idea. Since we don’t know who produced this or how to get in touch with them, we have no way of knowing.